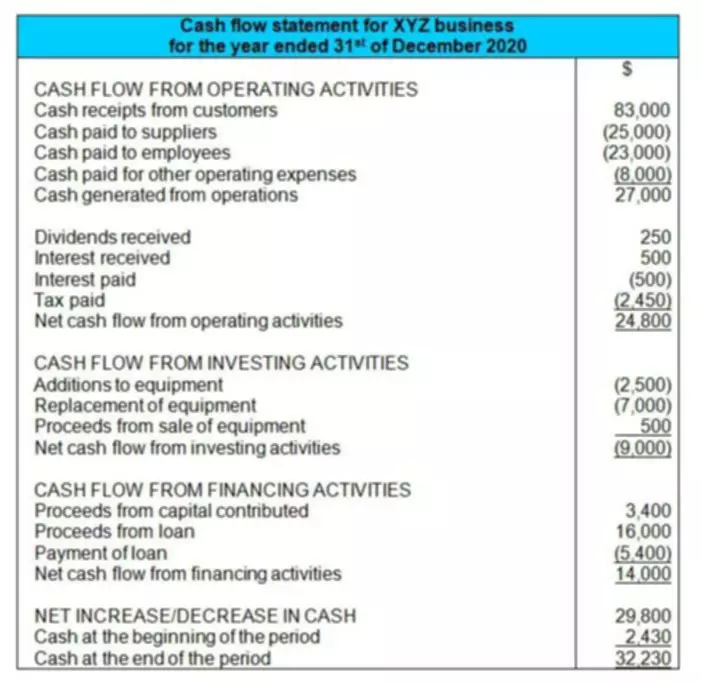
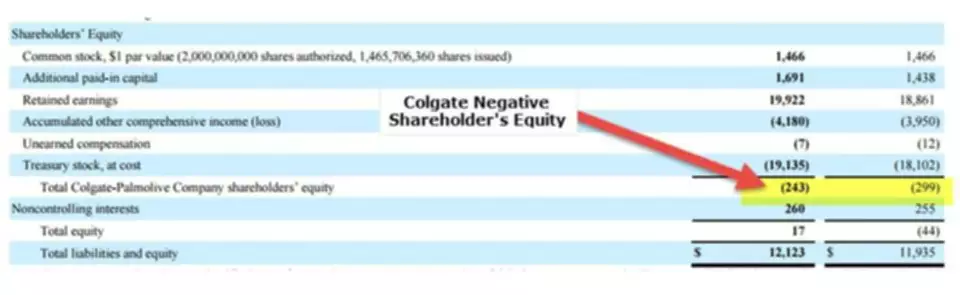
Content
Evidence in an audit includes all documentation and information that can be used to support the auditor’s opinion on each management assertion. Each class of transactions may have its own level of evidence required for a given assertion so auditors must determine which documents or pieces of data are relevant to their work. Evidence also refers to the tests that are performed to gather information about a particular class of transactions. For example, an audit of cash would include verifying the balance as well as reviewing cancelled checks and bank statements. Without classes there is no basis for planning, conducting or reporting on work performed. For example, a financial audit will have a series of classes such as cash, accounts receivable and inventory. The auditor must also decide the level of evidence to be gathered for each class which is then used in making an assertion about whether that particular account balance or item is free from material misstatement.
- An auditing technique that can be used to gather evidence regarding both existence and completeness as it applies to inventory illustrates the importance of the direction of the stated procedure.
- The preparation of financial statements is the responsibility of the client’s management.
- Auditors need to know what they’re looking for when they go through an audit because there are many different kinds of audits that can be performed on various entities under various circumstances.
- For example, they must ensure companies have recognized all items in fixed assets that they must have.
- Different audit assertions include completeness, existence, accuracy, occurrence, valuation, cut-off, rights and obligations etc.
Asset Accounts are one of the categories in the General Ledger Accounts holding all the credit & debit details of a Company’s assets. We’re firm believers in the Golden Rule, which is why editorial opinions are ours alone and have not been previously reviewed, approved, or endorsed by included advertisers. Editorial content from The Ascent is separate from The Motley Fool editorial content and is created by a different analyst team.
Assess the Risk of Material Misstatement at the Assertion Level
But the purpose of risk assessment is to provide planning direction. Therefore, we need to know the risk of material misstatement at the assertion level. For cash, maybe you believe it could be stolen, so you are concerned about existence. Or with payables, you know the client has historically not recorded all invoices, so the recorded amount might not be complete. And the pension disclosure is possibly so complicated that you believe it may not be accurate.
The Financial Accounting Standards Board requires publicly traded companies to prepare financial statements following the GAAP. The transactions summarized into the financial statements have actually occurred. Transactions have been appropriately presented within the financial statements and accompanying disclosures. This assertion confirms that the transactions, balances, events, and other similar financial matters have been correctly disclosed at their appropriate amounts. This type of assertion confirms that all the transactions have been classified and presented properly in the financial statements. Completeness, like existence, may examine bank statements and other banking records to determine that all deposits that have been made for the current period have been recorded by management on a timely basis.
What Are the Five Types of Audit Assertions? (The 5 Most Important)
Stakeholders use these financial statements for various reasons. Usually, they rely on the information presented in those statements for decision-making. I think, in the future, you’ll see more and more auditors testing controls because of automation. audit assertions Rather than using an inefficient approach—let’s audit everything—the auditor pinpoints audit procedures. In other words, they might use assertions different from those listed above, or the auditor could list each assertion separately.
- Additionally, notice the inherent risk for occurrence is assessed at high.
- Of these, the five audit assertions of significant importance are available above.
- Logically, the substantive procedures must now address all of these risks.
- These representations are commonly referred to as Audit Assertions, Management Assertions, and Financial Statement Assertions.
- The Structured Query Language comprises several different data types that allow it to store different types of information…
- In auditing expenses, the auditor knows that a risk of fictitious vendors exists.
It relates to ensuring transactions recorded in the accounts are at appropriate amounts. Through the income statement, accuracy can also affect the balance sheet. Similarly, they help auditors assess if financial statements present a true and fair view.
Audit Assertions for Investments
Completeness – All transactions and accounts that should be presented in the financial statements are so included. Thus, the truth & fairness of the financial statements is justified with help of audit assertions. Valuation assertion says that the value should be as per the relevant accounting framework. Few accounting standards also requires provision in case of unrealised loss. Thus, auditor needs to ensure that the value appearing on the face the balance sheet is appropriate. Completeness Assertion – All transactions, balances, events, and other matters that should have been disclosed have been disclosed in the financial statements.
Paragraphs of this standard describe specific audit procedures. The purpose of an audit procedure determines whether it is a risk assessment procedure, test of controls, or substantive procedure. Assertions are made by the management regarding the assets, liabilities, incomes, expenses, etc. Audit entity owns or controls the inventory recognized https://www.bookstime.com/ in the financial statements. Any inventory held by the audit entity on account of another entity has not been recognized as part of inventory of the audit entity. Financial accounting assertions are a very important part of auditing. That’s because there is no other way to hold the preparers of financial statements accountable.
Existence
Each also provides the assertion meaning or definition to help one understand how each is used in an assessment. The auditor will have to determine what level of evidence is needed in order to issue their opinion on each class including management assertions. Disclosed events, transactions, balances and other financial matters have been classified appropriately and presented clearly in a manner that promotes the understandability of information contained in the financial statements. All related parties, related party transactions and balances that should have been disclosed have been disclosed in the notes of financial statements. Transactions with related parties disclosed in the notes of financial statements have occurred during the period and relate to the audit entity.
Why is it important for small business owners to understand audit assertions?
The word “audit” can make anyone’s blood run cold. If you’re entering your financial transactions properly, you don’t have anything to be worried about. However, understanding what auditors are looking for can help to ease your panic.





